Table of Contents
Introduction
Risk management is widely regarded as the most important skill a trader can develop, yet it remains one of the most misunderstood and underestimated aspects of trading, particularly among beginners who often focus exclusively on entries, indicators, or strategies while ignoring the mechanisms that actually determine long-term survival. Although finding high-probability setups is important, no trading strategy—no matter how sophisticated—can produce consistent results without a structured approach to controlling risk.
Professional traders do not succeed because they win every trade, nor do they rely on perfect market timing or prediction; instead, they remain profitable because they understand how to limit losses, preserve capital, and stay active in the market long enough for probability and discipline to work in their favor. Risk management is therefore not about eliminating losses altogether, but about ensuring that losses remain controlled, predictable, and incapable of causing permanent damage to a trading account or to a trader’s psychological stability.
This guide is designed to provide a complete, practical, and beginner-friendly explanation of trading risk management, covering not only the technical rules used by professionals but also the mindset required to apply those rules consistently. By the end of this article, you will understand how to protect your trading capital from day one, how experienced traders think about risk before entering a position, and how to build a sustainable approach that prioritizes longevity over short-term excitement.
1. What Is Risk Management in Trading?
Risk management in trading refers to the structured process of identifying, measuring, and controlling potential losses before a trade is ever executed, rather than reacting emotionally after the market has already moved against you. It defines how much capital you are willing to risk on a single idea, where the trade thesis becomes invalid, and how position size should be calculated so that no single outcome can significantly harm your account.
At its core, risk management answers three fundamental questions that every trader must be able to answer with clarity before clicking the buy or sell button: how much money am I risking on this trade, where exactly will I exit if I am wrong, and does the potential reward justify accepting that risk. When these questions are ignored or answered vaguely, trading quickly turns into gambling; when they are answered precisely, trading becomes a structured business.
2. Why Risk Management Matters More Than Strategy
One of the most surprising realizations for new traders is that risk management often has a greater impact on long-term profitability than the trading strategy itself, because two traders using the exact same setup can experience dramatically different outcomes depending on how they manage risk. A trader who controls position size, respects stop-loss levels, and limits exposure during drawdowns will often outperform another trader who has better entries but lacks discipline.
Effective risk management allows traders to survive losing streaks without emotional collapse, maintain consistency during volatile market conditions, and compound gains gradually over time, rather than chasing large wins that expose them to catastrophic losses. For this reason, many professionals argue that risk management is not merely a supporting element of trading, but the strategy itself, since it governs every decision that follows.
3. Core Principles of Trading Risk Management
Risk management is built upon a small number of foundational principles that apply across all markets, timeframes, and trading styles, regardless of whether one is trading stocks, forex, commodities, or cryptocurrencies.
Capital Preservation Above All Else
The primary objective of any trader should not be to make money quickly, but to preserve capital so that opportunities remain available in the future, since a trader without capital cannot participate in the market at all. Protecting capital ensures longevity and allows learning to continue even during difficult periods.
Consistency Over Aggression
Aggressive risk-taking may feel exciting in the short term, but it dramatically increases the probability of account destruction, whereas consistent and controlled risk allows statistical edges to play out over hundreds of trades rather than a handful.
Losses as a Normal Cost of Business
Losses are an unavoidable part of trading, and professional traders accept them calmly because they are expected, predefined, and controlled, rather than emotional or impulsive reactions to market movement.
4. How Much Should You Risk Per Trade?
Determining how much to risk on a single trade is one of the most critical decisions a trader makes, and most professionals limit this amount to between one and two percent of total account equity in order to reduce drawdown severity and emotional pressure during losing streaks.
| Account Size | 1% Risk | 2% Risk |
|---|---|---|
| $1,000 | $10 | $20 |
| $5,000 | $50 | $100 |
| $10,000 | $100 | $200 |
| $50,000 | $500 | $1,000 |
By keeping risk per trade small and consistent, traders ensure that no single mistake can undo weeks or months of disciplined work.
5. Position Sizing and Risk Control
Position sizing is the mechanism through which risk rules are enforced in practice, as it determines how many shares, contracts, or lots are traded based on the distance to the stop-loss and the predefined risk limit. Correct position sizing ensures that risk remains constant even when market volatility changes.
Position Size Formula
Position Size = (Account Risk in Dollars) ÷ (Stop-Loss Distance)
This formula removes emotion from the decision-making process and replaces it with logic, ensuring that trades are sized according to risk rather than confidence or impulse.
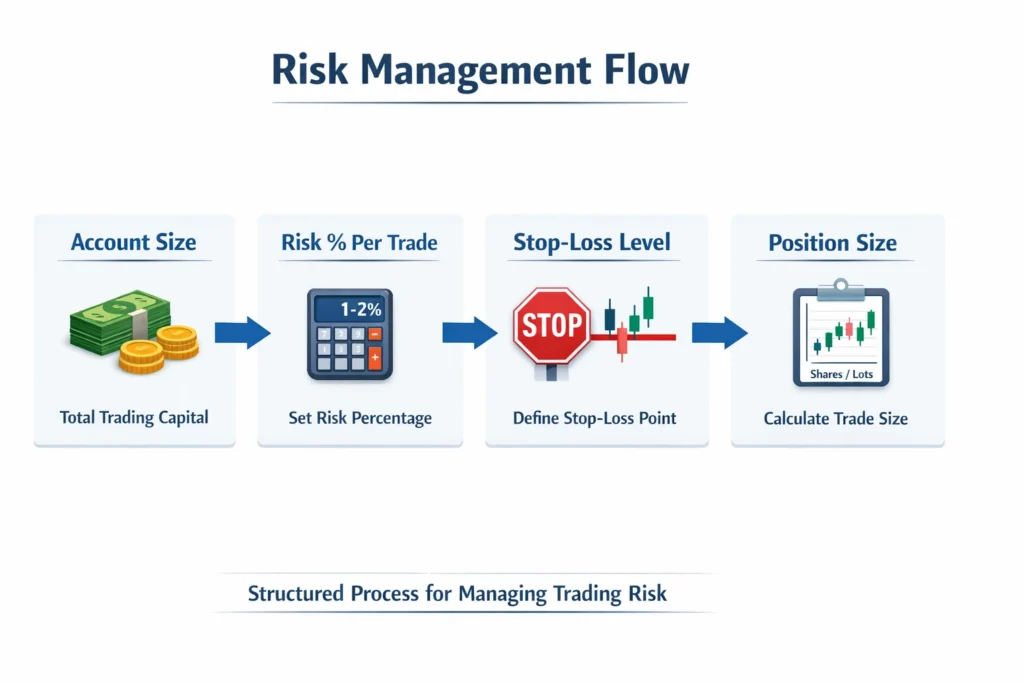
This diagram visually connects all components of risk management into one continuous process, making it easier for beginners to understand how professional traders structure decisions before entering a trade.
6. Stop-Losses as Capital Protection Tools
A stop-loss is a predefined exit level that automatically closes a trade when price reaches a point where the original trade idea is no longer valid, and it exists to protect capital rather than to limit profit potential. Traders who avoid stop-losses expose themselves to unlimited downside risk, which is incompatible with professional trading.
7. Risk-Reward Ratios and Probability
The risk-reward ratio measures how much potential profit is available relative to the amount of capital being risked, and it plays a crucial role in determining long-term expectancy, since traders can remain profitable even with relatively low win rates if reward consistently exceeds risk.
| Risk | Reward | Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| $100 | $100 | 1:1 |
| $100 | $200 | 1:2 |
| $100 | $300 | 1:3 |
8. Drawdowns and Account Survival
Drawdowns are inevitable in trading, but risk management determines whether they are survivable or destructive, as larger risk per trade leads to exponentially larger drawdowns that require unrealistic returns to recover from.
9. Emotional Risk and Discipline
Emotional mistakes such as revenge trading, over-trading, and moving stop-losses often stem from excessive risk, which increases psychological pressure and leads to poor decision-making under stress.
10. Linking Risk Management With Market Structure
Risk management becomes even more effective when combined with structural context, since understanding where a trade is invalidated allows for more logical stop placement and more consistent execution. For a deeper exploration of structure-based trade management, see our internal guide: What Is Market Structure? A Beginner’s Roadmap to Reading Price Like a Pro (2026 Master Guide)
11. External Learning Resources
For foundational context and broader financial principles, you may also consult Wikipedia’s Risk Management overview, which provides a neutral explanation of how risk control is applied across industries, as well as Investopedia’s guide to trading risk management, which offers practical examples relevant to active traders.
12. Risk Management Rules Every Professional Trader Follows
The risk management rules every professional trader follows are not random guidelines or optional suggestions but structured principles designed to protect capital across all market conditions, whether volatility is low, sentiment is optimistic, or uncertainty dominates price action. While technical tools such as stop-loss orders and position sizing form the mechanical foundation of risk control, professional traders rely on a broader framework of rules that govern how risk is applied consistently over time, ensuring that short-term outcomes never threaten long-term survival.
One of the most important risk management rules every professional trader follows is limiting total exposure across all open positions rather than focusing solely on individual trades, since multiple correlated positions can quietly magnify risk beyond acceptable levels. For this reason, experienced traders often define a maximum daily or session-based risk limit, commonly restricting total exposure to a small percentage of account equity, and immediately stepping aside once that limit is reached, regardless of how strong additional setups may appear.
Another rule that separates professionals from amateurs is the deliberate reduction of risk during drawdown periods, as sustained losses often signal either unfavorable market conditions or a temporary decline in execution quality. Instead of attempting to recover losses quickly by increasing position size, disciplined traders scale risk down, allowing both capital and emotional balance to stabilize before returning to standard risk levels.
Equally important is the refusal to increase risk after winning streaks, even when confidence is high and recent performance appears strong, because professional traders understand that consistency, not aggression, is what compounds capital over time. Finally, one of the most strictly enforced risk management rules every professional trader follows is absolute adherence to their trading plan, avoiding impulsive decisions, emotional exceptions, or untested setups, since long-term profitability is built on discipline and repeatability rather than isolated moments of confidence or fear.

External Learning Resources and Industry References
To further strengthen your understanding of professional risk management and place these concepts within a broader financial context, it is useful to consult established educational resources that explain how risk is managed across global markets. A widely trusted reference is the overview of risk management on Wikipedia, which explains how risk control principles are applied not only in trading but also in finance, economics, and corporate decision-making.
Traders may also benefit from reviewing Investopedia’s guide to risk management in trading, which provides practical explanations of position sizing, stop-loss usage, and capital preservation from a trading-specific perspective. Exploring these resources alongside the principles outlined in this guide helps reinforce best practices and confirms that disciplined risk management is a universal standard among professional market participants.
| Rule | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Daily risk limit | Prevents emotional overtrading |
| Reduced risk after losses | Controls drawdowns |
| Fixed risk per trade | Maintains consistency |
| No rule exceptions | Prevents emotional decisions |
FAQ: Risk Management in Trading
Is risk management more important than strategy
Yes, because risk management determines survival, while strategy determines opportunity.
What is the safest risk level for beginners?
Most beginners should limit risk to one percent per trade to allow room for learning.
What is the safest risk per trade for beginners?
Most beginners should risk no more than 1% per trade, allowing room for mistakes and learning.
Can I trade without a stop-loss?
Trading without a stop-loss exposes your account to unlimited risk and is not recommended for any trader.
Is risk management more important than strategy?
Yes. Risk management determines survival, while strategy determines opportunity.
What is the ideal risk-reward ratio?
Most professional traders aim for 1:2 or higher, depending on market conditions.
How do I control emotional trading?
Predefined risk rules remove decision-making pressure and reduce emotional reactions.
Conclusion
Risk management is the foundation upon which every sustainable trading career is built, as it protects capital, stabilizes emotions, and allows probability to work over time rather than forcing results through aggression. When risk is controlled, trading becomes structured, repeatable, and professional, transforming speculation into a disciplined process with long-term potential.

